Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty foods: 2025 FCC Food and Beverage Report

The following information is from the 2025 FCC Food and Beverage Report, which highlights the opportunities and challenges for Canadian food manufacturers by sector. To get the big picture, read the full report.
Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food manufacturers, whose products are typically more affordable than fresh foods (for example, canned and frozen), tend to do well when times are tough. Strained household budgets coupled with high food inflation, high interest rates and uncertain times have helped boost sales over the last three years. However, with both inflation and interest rates falling, sales are forecasted to fall -2.0% (Figure 1), while volumes (that is, sales adjusted for inflation) are expected to fall -6.5%, which aligns with volume sales in 2018 and 2019.
Figure 1: Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food sales to decline in 2025
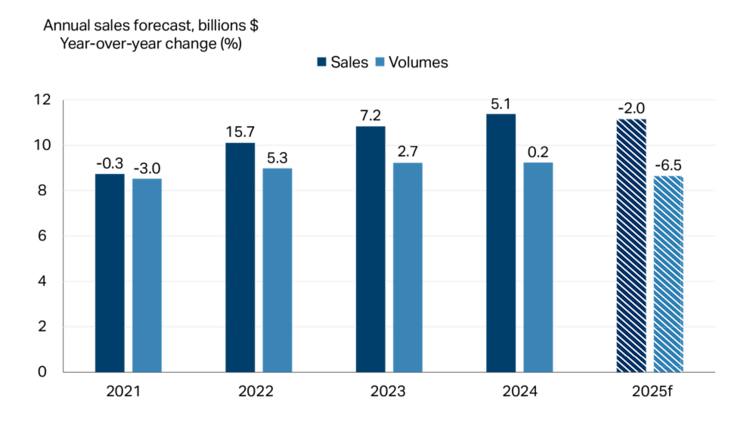
Total sales and volumes (in $, billions) are on the vertical axis and shown by the height of each bar. The number above each bar is the year-over-year growth as a percent. Volumes are sales deflated by a price index (202001=100).
Source: FCC Economics, Statistics Canada
While lower sales and higher labour costs add pressures to margins, raw material costs are expected to ease, giving a small boost to margins in 2025 (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food margins see some relief in 2025
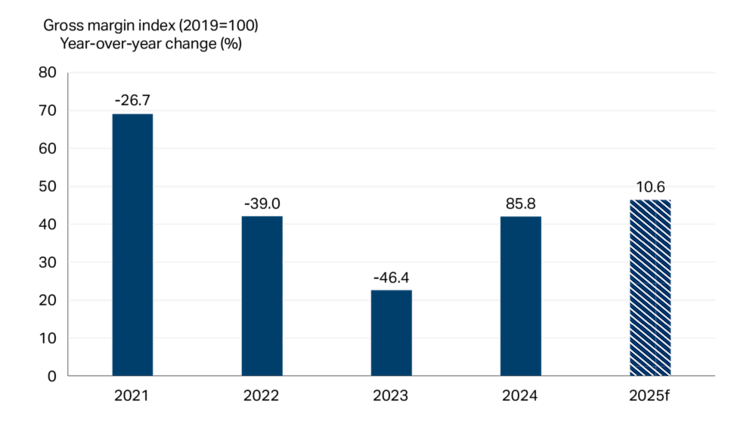
Sources: Statistics Canada, FCC Economics
Aside from the above-mentioned short-term challenges, the industry also must grapple with structural issues that continue to weigh on the bottom line. Fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food manufacturing was the only food manufacturing sector to record negative productivity growth between 2003 and 2023. Productivity has declined because businesses are usually labour intensive, small or medium-sized, or producing a wider variety of products. Established brands with strong recognition and loyalty among consumers continue to thrive and implement labour-saving technologies, while many small and medium-sized enterprises still rely on labour-intensive manufacturing processes.
Market insights: Keeping consumers interested in frozen and canned products
Frozen and canned products came into the spotlight in recent years as consumers looked for ways to save money during uncertainty, rising prices and high interest rates. Retail sales of frozen and packaged food rose faster than fresh in three of the last five years. On average, frozen and packaged food increased 7.3% per year compared to an increase of 5.7% for fresh food (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Frozen and packaged food sales at retail rising faster than fresh in three of the last five years
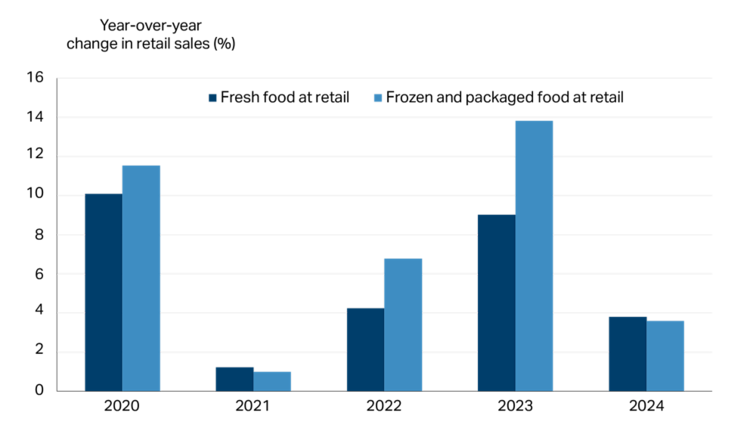
Source: Statistics Canada
As inflation slowed and interest rates eased into 2024, fresh food sales increased faster than frozen and packaged. The challenge for 2025 is for manufacturers to maintain consumer interest.
The two main categories of the fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food manufacturing sector are frozen food and fruit and vegetable canning, pickling, and drying. The sector’s opportunity is in its diverse offerings. Focusing on what consumers demand across the entire food and beverage space marks a perfect starting point for manufacturers. Following up by introducing innovative products can help the sector stay relevant.
Trends shaping consumer demand for food products in 2025
1. Convenience
Households continue to be strapped for time, and frozen food offers a solution. Marketing frozen foods as a pairing with fresh ingredients, as a quick snack or a full meal, appeals to a range of consumers for convenient and flexible meal preparation solutions.
2. Food waste
With a growing awareness of reducing food waste to align with sustainability interests or cost savings, canned and frozen products can extend shelf life and maintain quality longer than fresh.
3. High-low pairing
While focused on their budgets, consumers still enjoy restaurant-quality meals and luxury items. Frozen meals that deliver premium, restaurant-quality options or jellies and preserves that can add a touch of luxury without breaking the bank are an option to keep consumers interested.
4. Health
Consumers are interested in food that helps meet their health goals, such as managing weight, healthy aging and fitness. Focusing on creating products high in protein or fiber and low in sugar and sodium could appeal to some consumers.
Other trends to watch
Competition from imports continues to rise. In 2024, 55% of the domestic supply of fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food came from imported sources, up from 47% in 2014.
Canned and frozen foods rely on packaging to preserve products, many of which are imported from the U.S. and may face increased costs due to trade disruptions.
The fruit and vegetable preserving and specialty food manufacturing sector is especially vulnerable to trade disruptions as almost half of its sales come from the U.S. market, and profit margins have been thin in recent years. It would be difficult for the sector to pass on extra costs and/or manage through lower revenues.

